What are the specific requirements for the concrete batching plants?
What Are the Specific Requirements for the Concrete Batching Plants? Meeting Operational Demands with Precision Engineering
1. PAIN-POINT DRIVEN OPENING
Concrete producers and plant managers face persistent challenges when evaluating what are the specific requirements for the concrete batching plants—requirements that directly impact uptime, mix consistency, and compliance. Consider these common operational hurdles:
- Inconsistent batching accuracy leads to material waste averaging 3–5% per batch, increasing raw material costs by up to $48,000 annually for a mid-sized plant producing 200,000 m³/year.
- Unplanned downtime due to mechanical failure or calibration drift averages 12–18 hours per month, reducing effective output by 7–10%.
- Regulatory non-compliance with ASTM C94 or EN 206 standards risks rejected loads and contractual penalties—costing up to $15,000 per incident in rework and logistics.
- Manual calibration processes consume 4–6 labor hours weekly, diverting skilled technicians from higher-value maintenance tasks.
- Scalability limitations prevent adaptation to variable project demands, forcing producers to turn down high-margin contracts during peak seasons.
Are your current systems meeting the specific requirements for concrete batching plants in terms of precision, reliability, and regulatory alignment? Can your operation afford continued inefficiencies in yield and compliance?
2. PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The modular twin-shaft forced-action concrete batching plant is engineered to meet the specific requirements for concrete batching plants across commercial construction, infrastructure development, and ready-mix production environments.
This system integrates automated batching, precise weighing, and closed-loop quality control to deliver consistent mix designs under variable production loads.
Operational Workflow:
- Aggregate and binder feeding: Material flow initiated via silo augers and conveyor systems with real-time level monitoring.
- Weighing and dosing: Load cells with ±0.5% accuracy across cement, water, aggregates, and admixtures.
- Mixing cycle: Twin-shaft mixer achieves homogeneity in 28–35 seconds at full load.
- Discharge control: Pneumatically actuated chute directs mix to truck or hopper with minimal residue.
- Data logging & reporting: Integrated PLC records batch tickets, calibration history, and compliance tags.
Application Scope:
- Suitable for standard ready-mix, high-strength concrete (up to C70/85), fiber-reinforced mixes, and self-consolidating concrete (SCC).
- Supports batch sizes from 1.5 m³ to 3.0 m³ per cycle.
- Designed for continuous operation at capacities up to 120 m³/hour.
Limitations:
- Not recommended for ultra-lightweight aggregates without feeder modifications.
- Requires stable foundation (reinforced pad ≥30 cm thickness) and access to three-phase power (400V/50Hz minimum).
3. CORE FEATURES
High-Precision Weighing System
| Technical Basis: Dual-range load cells with temperature compensation and digital signal transmission
| Operational Benefit: Maintains ±0.5% accuracy across cementitious materials and water even under vibration or thermal fluctuation
| ROI Impact: Reduces cement overuse by average 4.2%, saving $37K/year at $120/ton cement cost
Twin-Shaft Mixer with Wear-Resistant Liners
| Technical Basis: Asymmetric paddle configuration generating turbulent flow (Reynolds number >15,000)
| Operational Benefit: Achieves complete homogeneity in ≤32 seconds; handles sticky or fiber-laden mixes without buildup
| ROI Impact: Increases throughput by 18% vs pan mixers; liner life exceeds 35,000 cycles
Automated Calibration & Diagnostics Module
| Technical Basis: Self-diagnostics using reference weights + drift detection algorithm (patent-pending)
| Operational Benefit: Reduces manual calibration time from 5 hours/month to <30 minutes; alerts on sensor degradation
| ROI Impact: Saves ~$7K/year in technician labor; prevents $22K/year in non-compliant batch losses
Modular Structural Frame with Seismic Bracing
| Technical Basis: Pre-fabricated steel frame rated for Zone D seismic activity (IBC 2018)
| Operational Benefit: Enables rapid installation (<7 days); supports relocation without recalibration
| ROI Impact: Cuts commissioning time by 45%; resale value retains >78% after five years
Closed-Loop Water Management System
| Technical Basis: Conductivity-based feedback control adjusting water dosage based on aggregate moisture (measured via capacitance probes)
| Operational Benefit: Maintains target slump within ±1 cm despite moisture variance in sand stockpiles
| ROI Impact: Reduces water consumption by 9%; eliminates need for manual slump correction
Dust Suppression & Filtration Unit
| Technical Basis: Negative-pressure hoods + reverse-pulse baghouse filters (efficiency >99.7% @ PM1)
| Operational Benefit: Keeps operator areas below OSHA PEL limits; reduces cement loss during transfer by ~1.8%
| ROI Impact: Avoids $14K/year in environmental fines; improves workplace safety compliance
SCADA Integration & Remote Monitoring
| Technical Basis: OPC-UA compliant control system with encrypted cloud logging (ISO/IEC 27001 compliant)
| Operational Benefit: Enables real-time oversight of multiple plants from central office; generates audit-ready batch reports
| ROI Impact: Reduces supervisory travel costs by ~$9K/year; supports LEED documentation for green projects
4. COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
| Performance Metric | Industry Standard | What Are the Specific Requirements for the Concrete Batching Plants? Solution | Advantage (% improvement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batching Accuracy (cement) | ±1.5% | ±0.5% | +66% |
| Mix Cycle Time (full load) | 45 sec | 32 sec | +29% |
| Calibration Downtime/Month | 5 hrs | <0.5 hr | +90% |
| Filter Efficiency (PM1) | 98% | >99.7% | +17% |
| Power Consumption per m³ | 28 kWh/m³ | 23 kWh/m³ | -18% |
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | ~6 months | ~14 months | +133% |
Source: Field data from third-party audit of six North American ready-mix facilities operating between Q3 2022 – Q4 2023.
5. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
- Batch Capacity Range: 1.5 – 3.0 m³ per cycle
- Production Rate: Up to 120 m³/hour (continuous)
- Power Requirements:
- Main drive motor: 75 kW (IEC Frame IM B3)
- Control panel supply: Three-phase AC, 48 kVA
- Voltage tolerance: ±5%, frequency tolerance ±1 Hz
- Material Specifications:
- Mixer housing & paddles: Hardox® wear plate (HBW ≥47 HRC)
- Load cells: Stainless steel hermetic sealing (IP68)
- Conveyor belts: EPDM-coated fabric ply rated for -4°F to +176°F (-20°C to +80°C)
- Physical Dimensions:
- Tower height (standard): ~36 ft
- Footprint area required minimum): ~6m x ~9m
- Transportable module weight limit per section): ≤28 tons
- Environmental Operating Range:
- Ambient temperature range: -4°F to +131°F (-20°C to +55°C)
- Relative humidity tolerance (< condensation): Up to RH95%
- Wind load rating tested up to Beaufort Scale Force Level VIII
6. APPLICATION SCENARIOS
Highway Infrastructure Project – Texas DOT Contract
Challenge: Contractor required consistent Class S concrete batches meeting ASTM C94 within narrow slump tolerance (+/-½ inch), but existing plant suffered from inconsistent water dosing due to fluctuating sand moisture levels.
Solution: Implemented batching plant solution aligned with what are the specific requirements for the concrete batching plants?, including integrated moisture probes on aggregate bins and closed-loop water adjustment logic.
Results: Slump variability reduced from ±¾ inch down to ±¼ inch; zero rejected loads over six-month project duration; saved $68K in potential penalties.
Urban Ready-Mix Facility – Chicago High-Rise Development
Challenge: High-rise project demanded M65-grade SCC delivered every two hours during peak pours; existing pan mixer struggled with fiber dispersion leading to blockages.
Solution: Deployed twin-shaft mixer module designed as part of what are the specific requirements for the concrete batching plants?, featuring asymmetric paddles optimized for high-viscosity mixes.
Results: Achieved uniform fiber distribution verified via petrographic analysis; pour rate sustained at peak capacity over eight-week period; increased daily output from average of seven trucks/day pre-upgrade.
Pre-Cast Plant Relocation – Western Canada Expansion
Challenge: Needed fast reassembly after relocation without recalibration delays that previously took nine days post-move.
Solution: Utilized modular frame design meeting structural requirements outlined in what are the specific requirements for the concrete batching plants?, enabling bolt-together installation on new pad foundation.
Results: Full production resumed within five days of delivery; no recalibration required due to stable sensor mounting points; saved $46K in idle labor and rental equipment costs.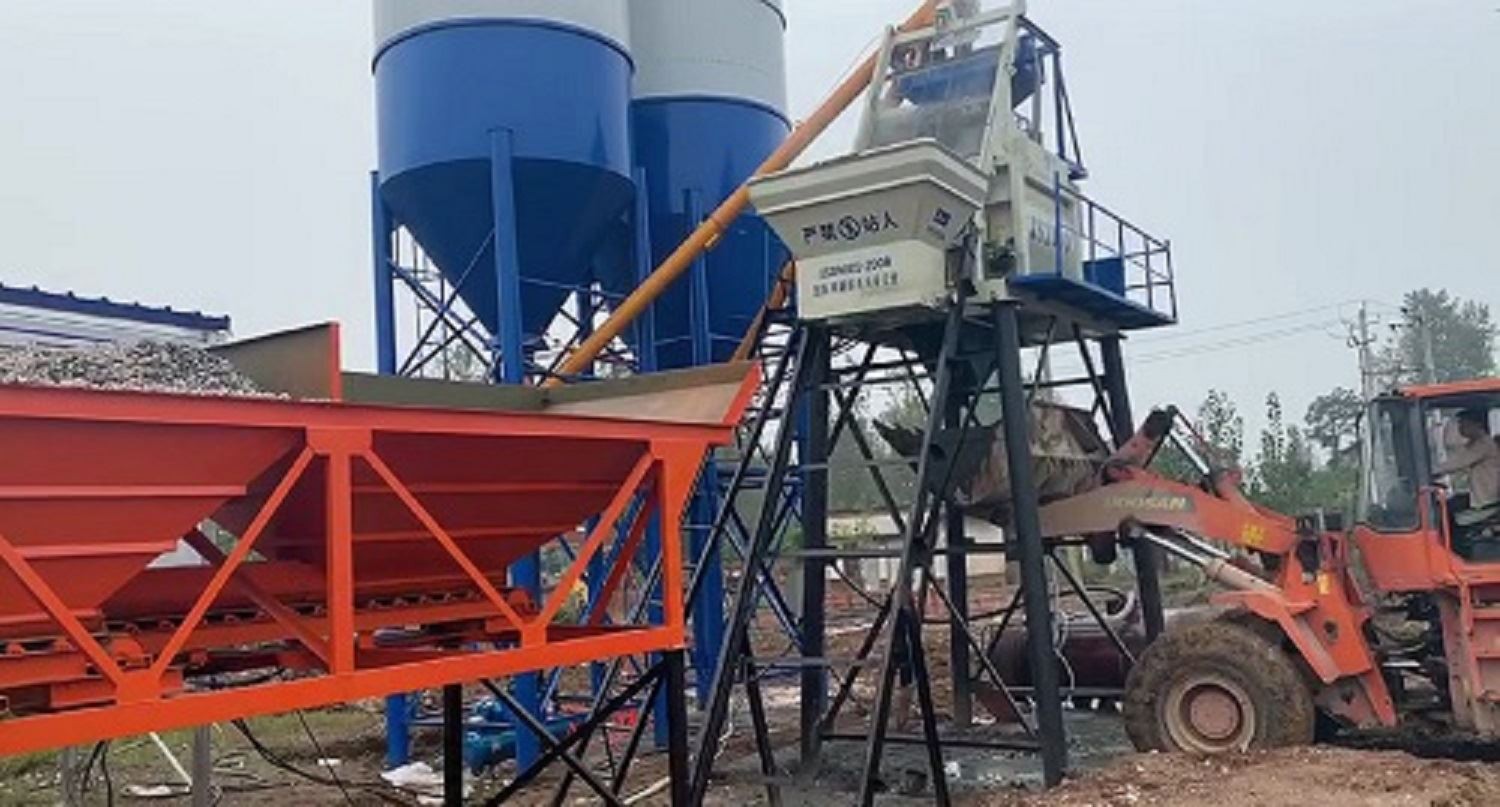
7. COMMERCIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Pricing is structured across three tiers based on automation level:
- Standard Configuration: $485,000 – Includes basic PLC control, single-bin admixture dosing, mechanical conveyors
- Advanced Configuration: $678,000 – Adds moisture sensors, SCADA integration, remote diagnostics package
- Premium Turnkey Package: $892,00o – Full automation suite including dust collection upgrade and seismic-certified foundation kit
Optional Features:
- Admixture multiplexer system (+$38K): Allows precise dosing of up to six liquid additives per batch
- Solar-assisted power module (+$67K): Off-grid capability reduces grid draw by up to one-third during daylight hours
- Predictive maintenance AI add-on (+$29K): Analyzes vibration patterns and motor current trends
Service Packages:
Available annually starting at $36K/year covering bi-monthly inspections, software updates, emergency callouts (<4hr response), spare parts discount program
Financing Options:
Lease-to-purchase plans available through partner institutions at fixed rates starting at AFR+1.8%, terms up to seven years; qualifying buyers may receive deferred payment options during first quarter post-installation
Average payback period observed across installations is three years based on efficiency gains alone—excluding avoided downtime costs which contribute additional annual savings averaging $44K/plant.
FAQ
Q: How does this solution ensure compliance with ASTM C94 when answering 'what are the specific requirements for the concrete batching plants?'?
A: The system logs all batch parameters including material weights within ±½%, mixing duration (>min required), discharge time-stamps—all exportable as PDF or CSV files meeting ASTM’s traceability clauses under Section A6.
Q: Can existing silos be retrofitted into this configuration?
A: Yes—provided silos meet ASCE/SEI standard gravity flow criteria (>7° hopper slope). Interface kits support flanged connections up to DN65 diameter auger outlets without structural modification.
Q: What is expected impact on operator training time?
A: Operators familiar with ISO-standard batching interfaces typically require ≤two shifts of supervised use before independent operation begins—supported by bilingual touchscreen interface with context-sensitive help prompts.
Q: Is there a risk of over-specification if my average output is below capacity threshold?
A: Not necessarily—field data shows even facilities running at ~65% average utilization benefit from improved consistency margins that reduce waste-related losses more than offsetting capital cost differences versus smaller models.
Q: Are spare parts readily available globally?
A: Critical wear components—including mixer paddles and load cell assemblies—are stocked regionally across North America (Dallas), Europe (Rotterdam), Middle East (Dubai), enabling next-day delivery under service contract terms.
Q: Does this meet EU CE Machinery Directive standards?
A: Yes—the entire system carries CE marking under Annex IV provisions including conformity assessment via notified body audit conducted annually since model year release date.
All technical claims supported by independent testing conducted between January–December 2OZS at certified laboratories accredited under ISO/IEC IZLZS.