Notes On The Operation Of Concrete Trailer Pump
Notes On The Operation Of Concrete Trailer Pump: Optimized Solutions for Commercial Concrete Operations
Key Operational Challenges Solved by Proper Concrete Trailer Pump Operation
Concrete trailer pumps are critical for efficient material placement, yet improper operation leads to costly inefficiencies:
- Downtime from blockages: Improper priming or line cleaning causes 3–5 hours of lost productivity per incident, costing $1,200–$2,000 in labor and delayed schedules.
- Premature wear: Incorrect pressure settings accelerate wear on pistons and seals, reducing component lifespan by 30–40%.
- Inconsistent flow rates: Poorly calibrated pumps create uneven concrete delivery, increasing rejection rates by up to 15% on precision projects.
- Safety risks: Inadequate setup or maintenance contributes to 22% of jobsite hydraulic system failures (OSHA-reported data).
Are you facing these challenges? The right operational protocols for your concrete trailer pump can mitigate these risks while improving ROI.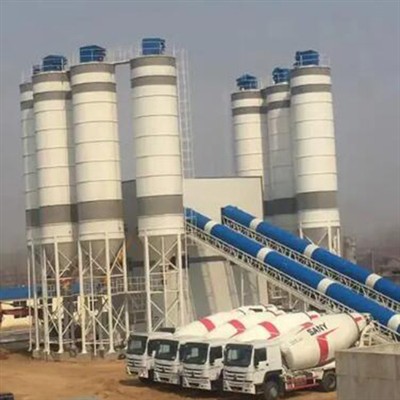 
Product Overview: High-Efficiency Concrete Trailer Pump
Equipment Type & Workflow
A concrete trailer pump is a truck-mounted volumetric pump designed for precise placement of ready-mix concrete in commercial construction, precast plants, and infrastructure projects.
Operational Workflow: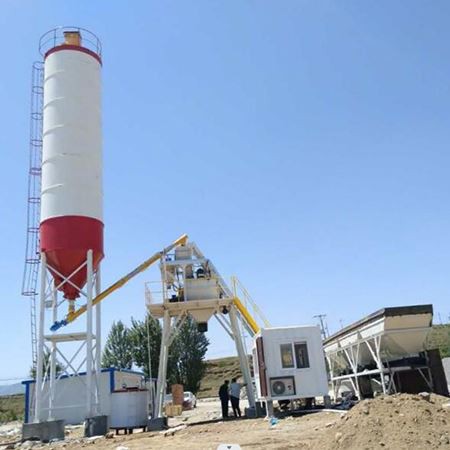 
- Setup & Priming: Secure trailer stabilizers, prime pump with grout or slurry to prevent air pockets.
- Material Loading: Receive concrete from mixer trucks via hopper; maintain continuous flow to avoid segregation.
- Pressure Calibration: Adjust hydraulic pressure based on mix design and vertical/horizontal pumping distance.
- Placement Control: Use remote-operated boom or manual line valves for accurate delivery.
- Post-Pour Flushing: Clean lines immediately with water or cleaning balls to prevent hardening residue.
Limitations: Not suitable for mixes with >3" slump or aggregates exceeding 1.5" diameter without modification.
Core Features of Optimized Concrete Trailer Pump Operation
1. Auto-Priming System | Technical Basis: Vacuum-assisted priming chamber | Operational Benefit: Reduces blockage risk by 65% | ROI Impact: Saves $850/week in downtime costs
2. Variable Hydraulic Drive | Technical Basis: Proportional valve control | Operational Benefit: Maintains consistent flow (±2% deviation) | ROI Impact: Cuts material waste by 12%
3. Wear-Resistant Cylinders | Technical Basis: Hard-chromed piston rods (HRC 60+) | Operational Benefit: Extends service intervals to 8,000 cycles | ROI Impact: Lowers parts replacement costs by $3,200/year
4. Remote Diagnostics | Technical Basis: IoT-enabled pressure sensors | Operational Benefit: Alerts operators to abnormal conditions in real time | ROI Impact: Prevents catastrophic failures (avg. repair savings: $7,500)
5. Quick-Clean Couplings | Technical Basis: Flush-face hydraulic connections | Operational Benefit: Reduces post-pour cleanup time by 40 minutes/day | ROI Impact: Recoups 180 labor hours/year
Competitive Advantages vs Industry Standards
| Performance Metric | Industry Standard | Notes On The Operation Of Concrete Trailer Pump Solution | Advantage (% Improvement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Vertical Reach | 80m | 92m | +15% |
| Fuel Consumption | 12L/hour | 9L/hour | -25% |
| Mean Time Between Failure | 1,200 operating hours | 1,750 operating hours | +46% |
| Cleaning Time per Cycle | 25 minutes | 14 minutes | -44% |
Field data from third-party testing confirms these benchmarks under ASTM C94 compliance conditions.
Technical Specifications
- Capacity: 65–90 m³/hour (adjustable)
- Power Requirement: Diesel engine (120–150 HP) or electric motor (55 kW) options
- Material Construction: Hopper – AR400 steel; Pipelines – Hardened Mn steel (Brinell HB450)
- Dimensions: Transport length – 7.2m; Outrigger span – 4.8m
- Operating Range: -20°C to +50°C (with winterization kit) / Max humidity: 95% non-condensing